Exercise 3
1. complete
- Static review objectives include
......,....., and...... - It is very useful that test basis has measurable coverage criteria to be used as
...... - An element of human psychology called
......makes it difficult to accept information that disagrees with currently held beliefs. - Static testing types include
......,......,......, and....... - Acceptance testing of system by administration staff is usually performed in a
...... - Finding defects is not the main focus of
......testing, its goal is to build confidence in the software. - Maintenance testing involve planned releases and unplanned releases called
....... - Triggers for software maintenance include
......,......and....... ......testing is used by developers of commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) software who want to get feedback from potential/existing users, customers before the software product is put on the market.
finding defects - gaining understanding - educating participantskey performance indicator (KPI)confirmation biaspeer revuew - walkthrough - technical review - inspection(simulated) production environmentuser acceptancehot fixesmodification - migration - retirementbeta and alpha
2. Explain the testing principles in details.
- testing shows the presence of defects
testing shows that defects are present but cannot prove that there are no defects
- exaustive testing is impossible
testing everything is impossible
- defect clustering
smaller number of modules usually is responsible for most of the perational failures
- early testing
to find defects early start testing as early as possible in SDLC
- pesticide paradox
repeated tests will no longer find more defects
- testing is context dependent
done differently in different contexts (safty-critical vs e-commerce system)
- abasence of error fallacy
fixing defects does not help if the system built is unusable
3. Identify three guidelines to successful conduct of review process.
- clear predefined objectives and measurable exit criteria
- the right people are involved
- testers a valued reviewers
- any checklists are up to date
- management supports a good review process
4. Clarify the tester role during each of SDLC phases. (not answered)
5. What should a tester do in case a component is not finished and he needs to conduct component integration testing?
Use driver
6. Compare between regression and confirmation testing types.
- confirmation testing
part as defect fix verification
- after the defect is detected and fixed, the software should be re-tested
- regression testing
testing the system to check that changes have not broken previously working code
- re-run every time a change is made
- some fixes may preduced unintended side-effects that are called regressions
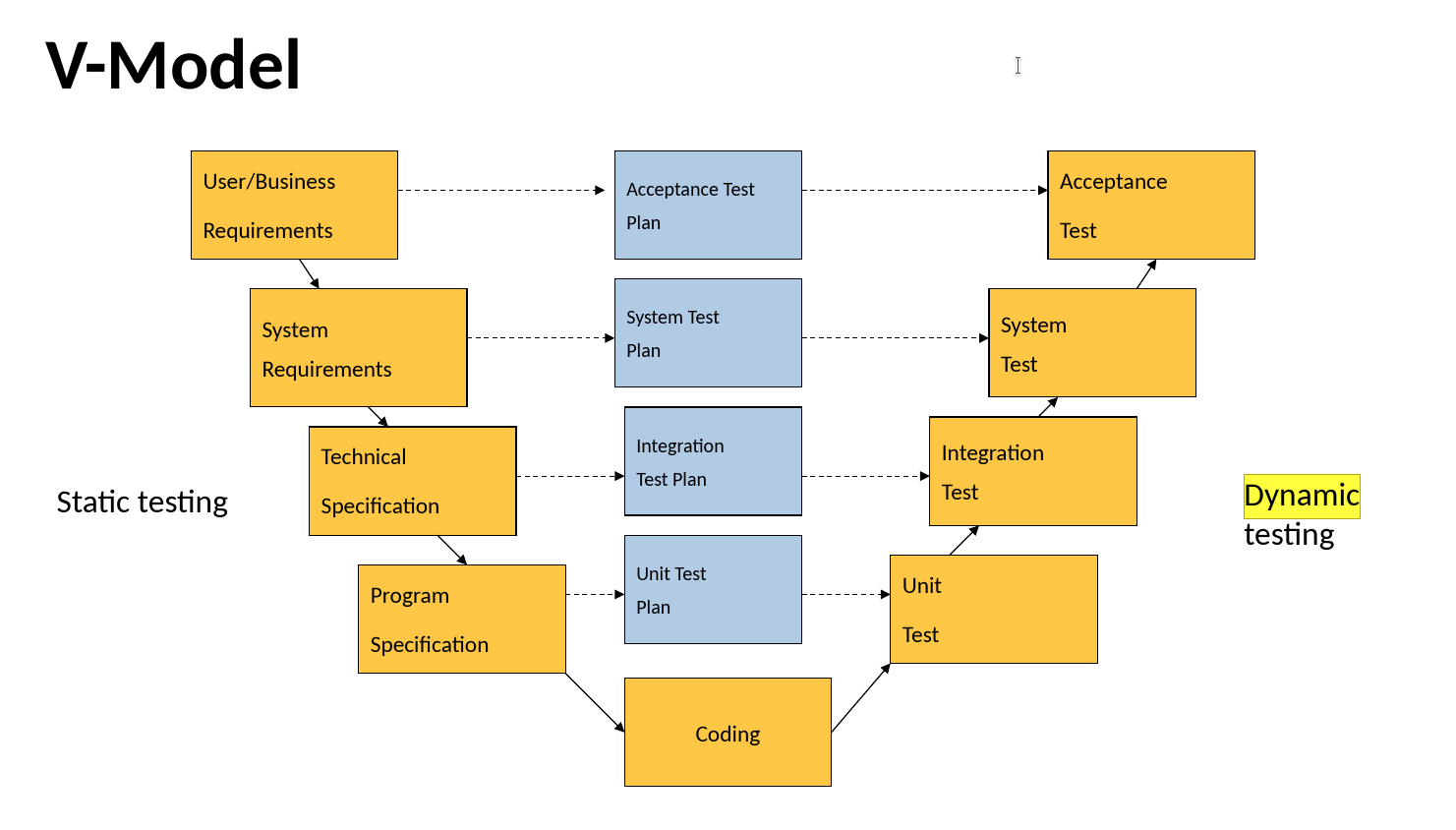
7. Illustrate steps of dynamic testing using a diagram.
8. Specify Formal Review/Inspection Activity
- Evaluating the review findings against the exit criteria to make a review decision
- Explaining the scope, objectives, process, roles, and work products to the participants
- Noting potential defects, recommendations, and questions
- Defining the entry and exit criteria
- Review meeting/issue communication and analysis
- Initiate review
- Individual preparation
- Planning
9. Whose Responsibility in Review?
- Document all the issues, problems, and open points that were identified during the meeting. With the advent of tools to support the review process, especially logging of defects/open points/decisions, there is often no need for a scribe
- Decide on the execution of reviews, allocates time in project schedules and determines if the review objectives have been met
- Lead, plan and run the review. May mediate between the various points of view and is often the person upon whom the success of the review rests
- scribe
- manager
- moderator/facilitator
10. Specify Review Technique
- Reviewers are provided with structured guidelines on how to read through the work product based on its expected usage.
- Reviewers detect issues based on set of questions based on potential defects, which may be derived from experience.
- Reviewers are provided with little or no guidance on how this task should be performed. It needs little preparation and is highly dependent on reviewer skills.
- Reviewers take on different stakeholder viewpoints in individual reviewing.
- Scenario-based/dry run.
- Checklist-based.
- Ad hoc.
- Perspective-based reading.
11. In Which Testing Level Can Defect be Found?
- Incorrect sequencing or timing of interface calls
- Incorrect in code logic
- Failure of the system to work properly in the production environment(s)
- Integration testing
- Component testing
- System testing
12. Replace with Key Term(s)
- Most formal review type, Led by the trained moderator, involves peers to examine the product, The defects found are documented in a logging list or issue log.
- Testing without having any knowledge of the interior workings of the application.
- is the detailed investigation of internal logic and structure of the code, also called: glass testing or open-box testing.
- Tests that evaluate functions that the system should perform.
- is the process of testing individual components in isolation.
- focuses on interactions and interfaces between integrated components. It is generally automated. It is often the responsibility of developers.
- focuses on interactions and interfaces between systems and packages. It is the responsibility of testers.
- a level of testing that validates the complete and fully integrated software product.
- is a stage in the testing process in which users provide input and advice on system testing.
- Users of the software test the software in a lab environment at the developer’s site.
- made available to users to allow them to experiment and to raise problems that they discover in their own environment.
- is performed against a contract’s acceptance criteria for producing custom-developed software. Acceptance criteria should be defined when the parties agree to the contract.
- is performed against any regulations that must be adhered to, such as government, legal, or safety regulations.
- is the testing of “how well” the system behaves, It involves testing a software for the requirements which are non-functional in nature but important such as performance, security, scalability, etc.
- It is a type of retesting that is carried out by software testers as a part of defect fix verification.
- It is possible that a change made in one part of the code may accidentally affect the behaviour of other parts of the code, whether within the same component, in other components.
Inspectionblack-box testingWhite-box testingfunctional testingComponent testingComponent integration TestingSystem integration testingsystem testinguser acceptance testing (UAT)Alpha testingBeta testingContractual acceptance testingRegulatory acceptance testingNon-functional testingConfirmation testingRegression testing